CIPD 3CO04 Essentials of people practice
- AC 1.1 Different stages of the employee lifecycle and the role of the people professionals in the lifecycle
- AC 1.2 Different ways in which information for specified roles can be prepared
- AC 1.3 Different recruitment methods and when is it appropriate to use them
- AC 2.1 Different selection methods and when it is appropriate to use them
- AC 2.4 Explain the selection records that need to be retained
- AC 2.5 Write letters of appointment and non-appointment for an identified role
- AC 2.2 Devise selection criteria for the post of People Assistant using the job description (Appendix A). Use the selection shortlisting matrix (Appendix B) to shortlist applications against the selection criteria to determine candidates to be interviewed.
- AC 2.3 Interview of one applicant and decide whether they meet the criteria for the post. The interview could be a panel or one-to-one interview. The interview could be conducted face-to-face, by telephone or by web conferencing.
- AC 3.1 An explanation of the importance of achieving work-life balance within the employment relationship with an overview of the regulations relevant to work-life balance.
- AC 3.2 An explanation of what is meant by, and the importance of, wellbeing in the workplace.
- AC 3.3 A summary of the main points of discrimination legislation
- AC 3.4 An explanation of what diversity and inclusion mean and why they are important
- AC 3.5 An explanation of the difference between fair and unfair dismissal
- AC 4.2 Explain the main factors that need to be considered when managing performance
- AC 4.3 Explain different methods of performance review
- AC 5.1 Explanation of key components (financial and non-financial) that are required to achieve an effective total reward system
- AC 5.2 Explanation of the relationship between reward and performance and the links to motivation
- AC 5.3 Reasons to Treat Employees Fairly In Retention to Pay
- AC 6.1 Explanation why learning and development activities are of benefit to individuals and organizations
- AC 6.2 Description of different types of learning needs and reasons why they arise for individuals and organisations
- AC 6.3 Summary of different face-to-face and blended learning and development approaches
- AC 6.4 Explanation of how individual requirements and preferences must be accommodated in the design and delivery of learning and development
- AC 6.5 Discussion of how learning and development can be evaluated
Task 1
AC 1.1 Different stages of the employee lifecycle and the role of the people professionals in the lifecycle
Employee life cycle is defined as every stage an employee goes through until they leave a job (Gupta, 2019). Employee lifecycle has 6 key stages; attraction, recruitment, on boarding, development, retention and separation (Cattermole, 2019).
- Attraction: A company will fail if they do not possess the right skilled labor no matter how good their product is. You need to promote and show your organization in such a way that people would feel content to work in such a place. As a people professional, my aim would be to ensure brand awareness is high, as a technology company endorsements with celebrities can also keep The organisation in limelight, making it as an ideal place to work.
- Recruitment: in this stage, you start your interviewing and assessing session, where you will include top skilled labor for your company. My part would be to refer a suitable candidate with problem solving and management skills to ensure the best for The organisation.
- On boarding: this involves training, orientation and providing overall support throughout the employees’ early days. Also induction and on boarding is necessary to ensure that the employees get familiar with their new role and the culture.
- Development: In this stage, the employee’s professional development is encouraged where the emphasis is on growth and skills advancement. Opportunities within the company are much appreciated.
- Retention: An important stage where the organization must ensure that the employees are satisfied and willing to work for long. In this regard, devising best strategies and performance appraisal would be an important aspect that I must cater to.
- Separation: the final stage where the employee concludes his journey in the organization can be due to retirement, or personal reason.
My main role in this lifecycle would be focused more on attraction and recruitment stage in order to filter out the high skilled management for the organisation.
AC 1.2 Different ways in which information for specified roles can be prepared
It is important to understand that recruitment is the process through which an organization’s HR department locates, attracts, selects, and recruits candidates to fill a position. Information is prepared in the different and stages of recruitment. According to CIPD (2020), the recruiting process consists of many stages:
- Job analysis – this phase is often referred to as the defining of the position. HR management conducts an analysis to determine the expected output, purpose, and fit with the business culture for a certain job holder at this phase (CIPD, Recruitment 2020).
- Job description: a statement of the hiring goals, duties, responsibilities, and expectations of a position holder. Additionally, the HR explicitly specifies the needed characteristics of the job holder.
- In the attraction phase, the organization announces the open job and puts a public advertising for the role.
- Application management: this comprises screening applications to exclude those that do not satisfy the basic standards.
- Selection: the process of conducting interviews and administering tests to choose the most qualified applicants.
- Hiring: gathering references, evaluating and approving medical data, and presenting a job offer, which results in contract signing
AC 1.3 Different recruitment methods and when is it appropriate to use them
There are different recruitment methods that have been documented and they are used differently:
a. Utilizing staffing agencies: this is the practice of outsourcing the recruitment process to a third-party agency on behalf of the employer. This strategy is appropriate for businesses without a dedicated human resources department. Additionally, it is ideal when a firm requires knowledge of a certain topic in order to finish the recruiting process (CIPD, Recruitment 2020). The procedure may not fulfill the organization’s personnel requirements.
b. Internal recruiting: this is the practice of employing employees from inside a company. This method is useful since it increases employee motivation, morale, and retention when they are aware of opportunities for career advancement. The strategy gives personnel who are already familiar with the company’s cultural practices. However, the method impedes the development of fresh ideas by external individuals.
c. Online recruiting using social media networks. Social Network Sites such as LinkedIn, a candidate monitoring system, or software-assisted interviews. This method is effective for recruiting candidates from a variety of areas. Additionally, it is a cheaper way of recruiting (CIPD, Recruitment 2020).
AC 1. 4 Factors to consider when deciding on the content of copy used in recruitment methods
The content of copy that is used in the recruitment methods depends on numerous factors. Audience whether internal or external: First, the content depends on the nature of recruitment, whether it is intended for internal or external audience. For the internal audience, the information could contain some privileged information that relate to the organisation. For instance, the mode of application could be sending a direct email that is different from the external one and the applicants may be required to quote a certain memo number (CIPD, 2020 Recruiment). In addition, the content for the internal audience may require that workers to have passed through some previous training as opposed to one that was external intended.
Cost of Recruitment: the content of the copy may also depend on the cost that is associated with the process of recruitment. For every recruitment method, there is a budget ceiling. As such, by sharing more information, it would mean that the cost would be higher (CIPD, 2020 Recruiment).
Contents
- 1 Task 1
- 2 AC 1.1 Different stages of the employee lifecycle and the role of the people professionals in the lifecycle
- 3 AC 1.2 Different ways in which information for specified roles can be prepared
- 4 AC 1.3 Different recruitment methods and when is it appropriate to use them
- 5 AC 1. 4 Factors to consider when deciding on the content of copy used in recruitment methods
AC 2.1 Different selection methods and when it is appropriate to use them
To fill vacant positions in a company, selection is the process of choosing the best qualified applicant with the necessary qualifications and skills from a pool of job applications. The human resources selection process can use a variety of methods to differentiate between qualified and unqualified individuals.
- References – In this strategy, a company solicits the advice of specialists in order to propose the most suitable individuals for certain roles. This technique is superior when you need to fill a job quickly yet want knowledgeable candidates from well-known experts (CIPD, Recruitment, 2020). Like psychometric testing, it is also a faster way of selection.
- Interviews – During an interview, applicants are given a score based on their responses to a series of questions. This strategy tries to gather candidate information to assist them in decision-making (CIPD, Recruitment 2020). This approach fails when dealing with a large number of applications. It is appropriate, however, for choosing applicants that need a panel of professionals to evaluate them due to their diverse skill sets.
- Psychometric testing: this is a process for determining a candidate’s mental and personality attributes via the administration of an aptitude test. This technique is suitable for finding candidates for technical professions requiring certain talents, such as inventiveness (CIPD, Recruitment, 2020) In contrast to interviews and group activities; this selection method is also more efficient.
AC 2.4 Explain the selection records that need to be retained
As part of the selection the following documents should be gathered and stored by the hiring organization:
- Resume/Curriculum Vitae: This document includes information on the applicant’s skills, experience, education, interests, professional certification, and hobbies. In addition, it highlights any honors the applicant has received in relation to the position being sought.
- Letter of Application: comprises the letter the candidate sent to demonstrate his or her interest in working for the firm. It also provides answers to some of the applicant’s questions about qualifications.
- Testimonials and certificates: both serve as evidence of academic performance. They also serve as evidence that the applicant received training or education. The fact that the applicant has worked for certain organizations is also a factor.
- Interview Outcomes: During an interview, the panel will evaluate the applicant based on their responses. As evidence of the applicants’ credentials, the interview findings should be recorded in the personnel files.
- Documents of identification: the candidate’s identification is submitted as proof of identity. These provide a person’s national and international identifying documents. The identity papers may consist of passports, national identification cards, and/or driver’s licenses.
- Letter of offer – the firm is obligated to maintain a copy of the contract letter after the employee has been chosen and legally hired.
AC 2.5 Write letters of appointment and non-appointment for an identified role
Appointment Letter
Dear Applicant
It is with congratulations that we notify you that you have successfully completed our evaluation and are eligible to join our organization. We congratulate you on your accomplishment and look forward to your contributions to the company. You are kindly requested to report to the organization’s manager on 12/512/2022, and you will be given specific instructions on the job you will be allocated. In order to accept our organization’s offer, you must sign the offer letter accompanied by the following documents:
1. National identity papers, such as a passport, driver’s license, or national identification card
2. Testimonials of your academic and other qualifications
3. Report of the Medical Examination
4. Bank account information
We anticipate working with you. If you may need any assistance or clarification before then, Please contact the human resources department at j.info@gmail.com if you have any questions.
Sincere regards
HR Manager
Rejection Letter
Dear Applicant
Thank you for submitting a job application that demonstrates your desire to work at our organization. We regret to notify you that we are unable to employ you at this time. Before picking the best applicant, we followed the same method with each application, which included screening, reference checks, and interviews. According to the evaluation, you were not the most qualified applicant for this position. This does not imply that you were unqualified, but the most qualified candidate was chosen.
We would want to emphasize that you were not rejected for the position due to incompetence, but it was a very competitive position. Therefore, we suggest you to continue visiting our career page for further for available opportunities. We also promise that your application will be maintained on file for five years and that you will be considered if a suitable position opens up during that time. In order to improve, we would also want to hear your comments on the whole recruiting process. Our Organization wishes you success in your professional endeavors.
Sincerely,
——————————————————————-
Human resources manager,
Task 2 Simulated interview
AC 2.2 Devise selection criteria for the post of People Assistant using the job description (Appendix A). Use the selection shortlisting matrix (Appendix B) to shortlist applications against the selection criteria to determine candidates to be interviewed.
Job Description is attached at appendix A
The short listing matrix is summarized in Appendix B:
AC 2.3 Interview of one applicant and decide whether they meet the criteria for the post. The interview could be a panel or one-to-one interview. The interview could be conducted face-to-face, by telephone or by web conferencing.
From the evaluation findings of the candidate short listing, I decided to have an interview with Johnson Brown for the post of People Assistant. I interviewed the candidate.
Thank you for joining us for the interview. We appreciate you coming in for the interview, and we are pleased to congratulate you on getting to this point in the selection process. You are aware that among the tasks of the People Assistant is the management of the workforce’s human resources, and it is possible that you may be expected to have skills and expertise pertaining to your function. I have a few questions for you, which will touch on both our professional and our personal relationships. Kindly reply to the questions to the best of your knowledge, but don’t feel obligated to answer if you don’t know the answer to any of the questions.
Interview Questions
- Please tell us more about yourself.
- Which of your many qualities do you regard to be your greatest asset that you bring to this organization ?
- If you had to choose one flaw in your character, what would it be?
- What are the three most important abilities you bring to the role of personal assistant?
- Could you please relate a recent instance in which you were responsible for the transformation of an organization?
- What kind of prior experience do you have in the function of PA?
- Could you please explain to the panel what you think your responsibilities are as a PA inside the organization?
- Could you please explain to the panel how you stay up to date on the latest concerns pertaining to people practice?
- Do you have any question for Us?
TASK 3 Guidance Document
AC 3.1 An explanation of the importance of achieving work-life balance within the employment relationship with an overview of the regulations relevant to work-life balance.
Definition of Work-Life Balance and Its Importance
To minimize the work in order to prevent stress and to establish a stable working way along with maintaining health and general well-being is known as work-life balance (WLB) (Poulose and Dhal, 2020). The importance of work-life balance entails that a good life balance for workers helps them increase staff retention rate, and motivation and reduces absenteeism as well as stress and working pressure. Moreover, a working-life balance attracts new talent and skilled employees to the firm. Figure 1 shows the importance of work-life balance (Haddon, 2018).
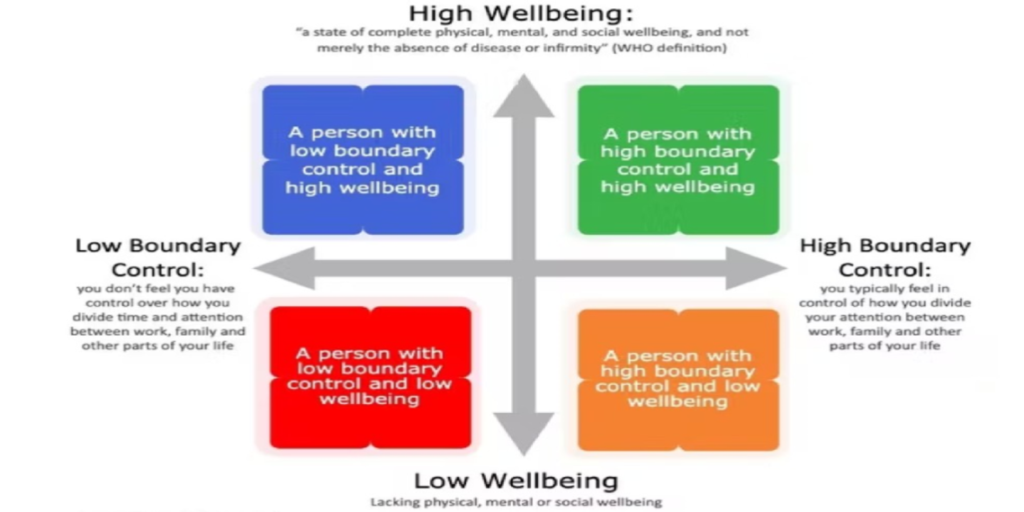
Figure: 1 Importance of Work-Life Balance
Source: (Mokhinur, 2020).
Regulations Relevant To Work-Life Balance
Working hours have been governed in the UK by legislation entitled “Working Time Regulations 1998 (CIPD. 2022-a)”. This legislation provides working hour limitations per week to the employees. The employees as per this legislation tend to work an average of 48 hours a week and a limit to work 8 hours per day. Employees contain the right to rest for about 11 hours per day and a day off at the weekend. This legislation assures that it is the responsibility of the employers to guarantee the safety of employees and provide them health safety by protecting them from the workload and overworking long hours (Pulakos et al., 2019). The term “Opting-out” (CIPD. 2022-c)” in legislation says that employers cannot force workers to work more than 48 hours a week. One of the reports published by CIPD showed that a healthy work-life balance facilitates workers in managing their time better (Diamantidis and Chatzoglou, 2018). Workers who hold specific public positions have the right to time off work to carry out their duties to serve the public under the “employment right act 1996”. For example, health body members, justice of the peace, academic institution governor, police authority member, etc. (Tziner and Rabenu, 2018).
AC 3.2 An explanation of what is meant by, and the importance of, wellbeing in the workplace.
Definition and Concept
Well-being in the workplace narrates all the working life features from physical environment safety and quality to the workers’ feelings regarding their work, environment, and culture of the organization (Cléry-Melin et al., 2019). A positive working environment promotes physical and also mental health. Some of the benefits of workplace well-being include a reduction in absenteeism and health care costs, an increase in employee engagement and dedication toward work, and improves employee productivity and morale (Nyarko, 2020).
Results of Not Paying Attention to It
If not paying attention to well-being in the workplace then it can contribute to physical and mental stress (Nguyen and Prentice, 2022). Physical and mental health contains a great contribution to well-being, the contribution of physical health in well-being manifests that as long as the human body is physically fit it tends to remain strong, whilst, mental health helps the body to sustain and achieve a good mental state. This as result helps the workforce to cope and handle stress and make healthy choices (Arifin et al., 2019). But the matter of fact is that it is the organizational and environmental pressures that affect wellbeing. At the workplace, employers sometimes ignore the need for employees’ well-being which raises the workplace problems like stress, conflicts, bullying, and even drug and alcohol abuse and mental health disorders as well. This results in declining in production and employee burnout (Kamalaveni et al., 2019).
Job design means the description of job roles including the duties and responsibilities of the job holder. Job design flexibility depends on the nature of the job. One of the principles of job design is not to risk the well-being of the job holder. Whilst, job analysis is to analyze the job design carefully, the misinterpretation of job design leads to workload. Job quality must be measured by understanding the strengths and weaknesses of the job. Job quality defines job design which benefits the individual and organization as well (Poulose and Dhal, 2020).
AC 3.3 A summary of the main points of discrimination legislation
Unjustified distinction action between workers on the basis of their race, age, religion, culture, sexual orientation, ethnicity, disability, etc. is termed as discrimination. The UK government has governed an act entitled “equality act 2010” in order to legally protect employees from discrimination (Haddon, 2018).
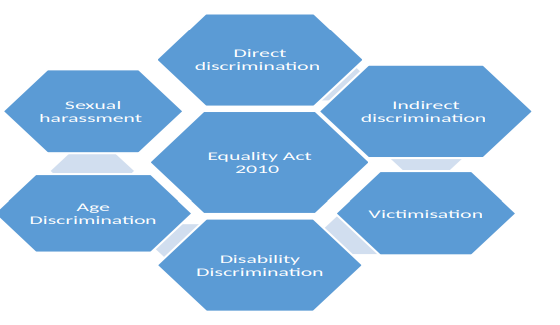
Figure 2: Protection through Equality Act 2010
Source: (Diamantidis and Chatzoglou, 2018).
Equality act 2010 contains the basic framework which assures the protection of workers at the workplace against direct discrimination, indirect discrimination, harassment, and victimization. The equality act 2010 defends against direct discrimination like sexual orientation, race, etc. Along with it, the law safeguards against indirect discrimination regarding religion, ethicality, age, gender, and more. It also guards the people discriminated against any endangered characteristics (Diamantidis and Chatzoglou, 2018). The act serves as indirect protection for people with disabilities. For people with disability, this act provides the flexibility to make reasonable adjustments while operating activities in the workplace. The equality act 2010 when applying the detrimental model facilitates to enhance the victimization protection.
The Act covers the protection of employees against harassment by third parties/individuals. It bans age discrimination in the workplace (Diamantidis and Chatzoglou, 2018). The implementation of discrimination legislation in an organization helps people professionals to raise voices against direct and indirect discrimination, sexual harassment, and victimization. The effective implementation of legislation to protect employees’ safety creates a trustworthy bond between employee and employer that ends up with increased productivity in an organization (Arifin et al., 2019).
AC 3.4 An explanation of what diversity and inclusion mean and why they are important
Diversity is the process in a workplace that recognize differences in order to accept employees of all background regardless of their race, ethicality, and color. Whereas, Inclusion in the workplace entails an environment that makes the employees feel valued and excludes discrimination (Poulose and Dhal, 2020).
In an organization, diversity and inclusion are highly linked with equal opportunity. Equality act 2010 emphasized and focuses on employers being liable to follow equal opportunity policies by providing equal join opportunities. They are obliged to treat all employees in an equal way based on their ability, and thus, must promote diversity and inclusion in the workplace regardless of employees’ sex, race, color, religion, disability, national origin, age, etc. (Cléry-Melin et al., 2019).
Diversity, inclusion, and equal opportunity contain significant importance in the workplace. It serves as beneficial in getting diverse viewpoints and experiences which raise the tendency to innovate and grow and thus ends up with increased revenue for an organization. According to one of the reports contained by CIPD, the organization that follows discrimination legislation like the discrimination act 2010, where employees feel safe, employees believe in social justice. The report shows that this organization’s employee retention rate tends to be 5.5 times higher than those who do not follow them (Pulakos et al., 2019).
AC 3.5 An explanation of the difference between fair and unfair dismissal
Fair dismissal is highly dependent on the code of conduct by employees which embraces the dismissal based on capability, performance, and other legal restrictions like hidden immigration status. The employee’s code of conduct contains many situations in which a company can use the right to dismiss the worker. For example, it may entail irreparable breakdown in trust and loyalty among employers and employees, and illegal activity in the workplace (Haddon, 2018).
Unfair dismissal is the termination of an employee that is not on the basis of the employee’s conduct. While talking about unfair dismissal various ground exists that depends on how the company legislation is enforced and in what country the origination exists, it all depends on where the company is based. An employee can be terminated on the ground of pregnancy unless they contain any leaves. An unfair dismissal can occur containing some reasons including, Paternity or maternity leave, Taking leave for caring dependents and Jury Service, Raising health and safety issues, and more (Nyarko, 2020).
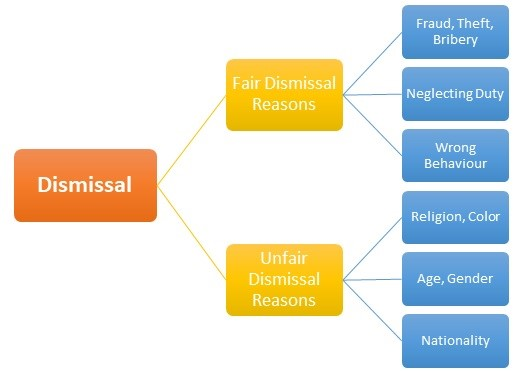
Figure: 3 Difference Between Fair and Unfair Dismissal
Source: (Simonsen and Shim, 2019).
TASK 4 briefing paper
AC 4.1 Explain the purpose and components of performance management
The main factors that influence performance management systems are; the working environment, Employee engagement level, social cohesion and Training, and Development opportunities. The company’s cultural environment includes a diverse and inclusive working environment. The employee engagement level embraces employee wellbeing policy, compensation, and ethical standard. Social cohesion includes interrelationships between employees (Arifin et al., 2019). The purpose of performance management is to improve the productivity of employees at their work which in return can increase the revenue of an organization (Nguyen and Prentice, 2022). The main components which put influence on performance management system are:
- Induction and socialization: this component emphasizes welcoming new employees and providing basic information about the company to help them process quickly and adapt themselves to the environment (Orridge and Madderson, 2021).
- Reviewing and appraising the performance: this component emphasized on Evaluation of the performance of an individual by identifying his strengths and weaknesses. Moreover, it provides feedback as well as set out goals to perform better.
- Reinforcing the performance standards: reinforcement supports the workers in improving their working standards (Cléry-Melin et al., 2019).
- Counseling and guidance for the employees: providing proper guidance and training improves the knowledge and skill of the workforce at their job place.
AC 4.2 Explain the main factors that need to be considered when managing performance
One of the factors is to create SMART and clear objectives to develop appropriate plans and strategies to achieve them (Nyarko, 2020). SMART objective includes, S= specific, M= measurable, A= attainable, R= relevant and T= time-bound. This factor has the tendency to inspire the team to work and collaborate. Another factor is to provide training for conflict resolution techniques. Thus, it is needed for employees and group members to learn how to cope with conflicts fairly and assertively (Nyarko, 2020). Moreover, the implementation of a value-based leadership style plays an important role in managing team performance. The leadership style in order to communicate clearly with team members is essential and needs to understand the expectations and needs of employees to perform best to increase their team performance productivity.
Needed Factors to Manage the Individual Performance
Feedback is the needed factor by the leaders to the employees avoiding all biasness helps an individual to increase his performance. They can thus evaluate their past performances with the present performances and can increase their productivity level (Cléry-Melin et al., 2019). Compensation and rewards are the factors that should not be ignored by the organization because it facilitates an individual with respect and dignity which provides him to feel motivated in the workplace and inspires them in performing their best in the workplace. A flexible working environment, work-life balance, and facilities of health and security also serve as helpful in improving and motivating an individual to increase their productivity and satisfaction levels at their workplace (Orridge and Madderson, 2021).
AC 4.3 Explain different methods of performance review
The role of appraisal is to provide peer feedback to employees and individuals on the basis of their performance. Appraisal plays an important role in performance management by allowing individuals and managers to exchange experiences, views, and opinions to modify their behaviors toward effective performance. Reinforcement helps employees improve their performance level and on the managerial level, it helps to provide future responsibility to them to increase productivity in comparison to their previous performances (Cléry-Melin et al., 2019).
Key Types of Appraisals
Annual Appraisal
This type of appraisal is presented yearly on the performance basis of an employee against the plans and targets of the firm. The feedback is given by managers with an aim to help the individuals with the set target plan in the future in order to increase performance (Arifin et al., 2019).
Formal Review
This type of appraisal is a frequent performance review in which employees’ formal records of performance are developed.
360 Degree
The company’s stakeholder gives various views and feedback on the individual’s employee performance with an aim to motivate them in the future.
Self-Assessment
Employees identify their own strengths and weaknesses and advance their personal characteristics in terms of performance and behavior to improve them (Pulakos et al., 2019).
AC 5.1 Explanation of key components (financial and non-financial) that are required to achieve an effective total reward system
An effective tool reward system embraces both financial as well as non-financial rewards for the workers to attain effective business objectives and goals. In financial benefits and rewards bonuses, incentives, pensions, performance appraisal pay job security, and promotions are included. On the other hand, in non-financial components, the total reward system is recognition, verbal appreciation, work-life balance (WLB) flexibility, and career development opportunities are included (Mokhinur, 2020).
A financial reward system helps in meeting the employees their day to day needs along with providing financial security to increase performance and productivity. Non-financial reward system helps reduce the physical and mental stress of employees. Recognition and respect increased the morale of employees and opportunities for career development boost knowledge and skills for future success. In sum, the effective total reward system facilitates an organization in retaining and attracting talent within the company. Also, boosts interpersonal relationships as a result of loyalty between employers and employees (Poulose and Dhal, 2020).
According to CIPD, a reward system should include the following components:
- Wages and Salaries: Compensation is seen in its whole as part of the total rewards model, and this encompasses not just the employee’s basic salary but also additional types of incentives that are designed to encourage workers to perform to the best of their abilities. It comprises the provision of a compensation package that provides additional financial as well as non-financial benefits in addition to the basic wage that is paid to the employee.
- Benefits: In accordance with the total incentives paradigm, businesses may try to offer benefits that go beyond the legally required minimums of Social Security contribution, paid sick leaves, and other allowances. This could be done in an effort to attract and retain employees.
- Flexible working: This encompasses comprehensive incentive program that allows for both adaptability at work and a healthy work-life balance for employees. The capacity of an individual to have a good balance between their home life and their professional life is referred to as “work-life balance.” In addition to that, it requires maintaining a healthy equilibrium between one’s personal and professional responsibilities. The following are some of the most common factors that contribute to an unhealthy work-life balance: a rising workload, working long hours, more responsibilities at home, and having a family.
- Recognition for great performance: Acknowledgement of outstanding performance is a component of a comprehensive incentive system, which also takes into consideration the recognition of high achievers. Career advancement In addition to monetary value, an individual’s total remuneration should take into account the availability of chances for their professional growth and development. They are inspired to work more and perform better as a result of this (CIDP. 2020. Strategic Reward and Total Reward).
AC 5.2 Explanation of the relationship between reward and performance and the links to motivation
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs embraces five elements as basic needs of employees at a workplace. Figure 4 illustrates the five basic needs to increase individual performance. The safety need, social needs, and esteem need come under an intrinsic reward system that helps individual to boost performance. In the meanwhile, physiological needs and self-actualization are fulfilled by extrinsic rewards (Pulakos et al., 2019).
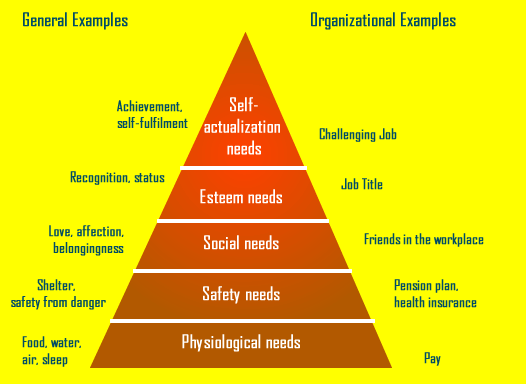
Figure 4: Maslow Hierarchy of Needs in Organizational Context
Source: (Tziner and Rabenu, 2018).
The relationship between reward and performance manifests that rewards are the motivation to perform well in an organization. Their relationship is directly proportional to one another. When the reward system is promoted it increases job satisfaction and indirectly increased the organization’s revenue and productivity as well (Pulakos et al., 2019). Intrinsic reward increases belongingness senses as a result employees get the motivation for continuous improvement. In sum, the reward acts as an intrinsic motivator in which employees feel valued and included and realise their contribution to bringing development to the firm. The extrinsic rewards (monetary rewards) promote job satisfaction and also increase employee performance and enhance retention and recruitment rate (Nyarko, 2020).

Figure 5: Relationship between Reward and Performance
Source: (Kamalaveni et al., 2019).
AC 5.3 Reasons to Treat Employees Fairly In Retention to Pay
The company must obey an equal pay structure along with minimized legal standards. There must be a national minimum wage because it will provide motivation to the employees in improving their performances. Not merely this it will help to increase the staff retention rate. Moreover, It has the tendency to increase the bonding and interpersonal relationship between employers and employees and can boost morale in this regard which will affect positively in terms of future success (Tziner and Rabenu, 2018).
Treating employee fairly may also mean providing appropriate remuneration. in light of this, if employees are offered higher pay than that offered by competitors, a large percentage of employees who remain with the company will grow. This will lower the amount of money spent on recruiting new employees and the amount of time needed to train them. (Shanock et al., 2019).
When workers are treated with respect, they are more likely to stay with the company; on the other hand, when they are not respected, the number of workers who leave the company rises (Shanock et al. 2019). It’s possible that employees might be motivated to boost their output. It’s a kind of drive that comes from inside. Treating employee fairly make the organisation the employer of choice, which attracts the best talented people. Potential workers are more likely to submit an application for a job that offers a higher beginning compensation than they are for a job that offers a lower beginning wage, which results in a significantly larger pool of candidates to choose from (Shanock et al. 2019).
TASK 5
Overview
The factsheet discusses the learning needs of employees and the organization as well as the factors (internal and external) which trigger the needs to learn and fill the gaps. It also identifies different methods and approaches of learning as well as the individual preferences of learning styles. It mentions the methods of designing and delivery learning materials to meet the needs and better understating of employees. Moreover, it discusses the qualitative and different models of evaluation of learning and development to measure the overall performance of employees and the organization.
AC 6.1 Explanation why learning and development activities are of benefit to individuals and organizations
Benefits to the Organization
- Improves retention: Career development helps firms retain great personnel. In reality, organizations consider training and development as a competitive advantage when recruiting.
- Builds Leaders: Targeting future leaders may help a company develop and evolve. New recruits or existing workers might be selected as management candidates.
- Increases employee productivity: Empowered leaders can better influence and acquire the confidence of their staff. Employees will experience more autonomy, worth, and confidence in their job.
- Increases employee engagement: Increasing employee engagement helps reduce workplace boredom, which can lead to unhappiness and poor work habits (Odor, 2018).
Benefits to Employee
- It boosts knowledge and skills: Training programs assist staff adapts to industry changes. These enhancements will boost worker productivity, increasing revenues and efficiency. Training may teach workers ethics, human relations, and safety.
- It meets performance-evaluation recommendations: When employee performance reviews show a need for improvement on a topic or ability, training programs might be established. Training can solve an issue.
- Employees advance and take on more tasks: Training programs may assist prepare workers for greater positions and additional responsibility. These programs will help them gain new job skills.
- Values workers: By teaching your staff new skills, they’ll become better workers and feel more productive. This will boost morale and productivity (Paine, 2021).
AC 6.2 Description of different types of learning needs and reasons why they arise for individuals and organisations
In order to improve engagement of employees, learning needs must be keenly observed (Caporarello, 2019). Learning needs arise when there is a gap between the skills required by the company in future and the skills the employee possesses. Both organization and employees might sometimes need to go through learning needs due to external and internal reasons.
External factors:
- Political: the changes in legislations can trigger learning needs for the organizations.
- Economic: Changes in consumer preferences can impose on devising new strategies
- Socio-cultural: Need to involve inclusivity of diversity.
- Technological: New machines or technology need learning and adaptation
- Environmental: New environment protection rules, for instance, more preference on the minimum use of plastic.
Internal factors:
- Gap in the performance and objectives of the company
- Needs to address future development (Jackson and Collings, 2018)
- Gap in the skill set required
- Professional development of employees
AC 6.3 Summary of different face-to-face and blended learning and development approaches
I. Facilitation:
Employees should be provided with proper resources and opportunities to find a follow their own learning route.
II. Consulting:
Consultation from internal and external consultants to identify the gaps must be provided by the organization to employees in order to blend learning.
III. Training:
Content based learning facilitated by an instructor to develop certain knowledge and skills regarding maybe a role, software or a new technology (Younas, 2018)
IV. Coaching
Coaching of employees is happened for overall improvement in performance. It mainly focuses on certain skills and goals and can aid in an improvement in personal attributes of an employee. It lasts for a certain and pre-defined period (CIPD, 2021c).
V. Mentoring
In mentoring, an experienced colleague shares their knowledge and skills with their juniors or inexperienced learning staff to provide support. It tends to be longer in terms of duration and is not restricted to a defined period (CIPD, 2021c).
AC 6.4 Explanation of how individual requirements and preferences must be accommodated in the design and delivery of learning and development
As per VARK framework, the learning design depends upon learning needs that must be catered to through the level of individual comfort; this involves flexibility, time, ethics and equality values (Srichailard, Wannasawade, and Sintanakul, 2019). The willingness an employee is willing to put in learning of new skills, knowledge and expertise is which is then facilitated by learning delivery, which is designed in a way to make employees learn and develop.
Key areas to observe for design and delivery of L&D:
- Identifying the learning preferences of individuals: VARK framework depicts different types of leaning styles, for instance, visual learners; tends to learn through shapes, images, diagrams, auditory learners; tend to learn through discussions recordings, lectures, kinesthetic learners tends to learn from demos and practices etc. Apart from that many other framework suggest that learners learn as per their leaning styles like theorists tends to learn from models, reflectors lean by watching, collecting info and evaluating the data
- Using a variety of learning methods (delivery): Many learning method inclusivity can broaden the minds of the employees in terms of expertise and can cater to all sorts of employees’ learning preferences such as active discussions, questioning sessions, presentation, etc.
- Use multiple resources: Likewise, the above stated learning methods inclusion of a variety of learning resources such as videos, practical, guest speaker sessions, tests and many other facilities could be used to attain maximum involvement from the individuals as per their learning approach. For instance, an individual requirement is to receive training regarding a new software system which was introduced in the organization. The training needs to be designed in such a way that the individual way is being catered, such as the employee in our scenario is a kinesthetic a learner, the training could be done in such a way that demo and practical are highlighted for the employee’s ease. In case of cultural differences or complex/ technical terms, the trainer is required to rephrase and explain and deliver training in an effective way. Monitoring of performance and suggestions must be made in order to work towards the improvement of the employee.
AC 6.5 Discussion of how learning and development can be evaluated
Evaluation is a basic necessity when L&D takes place in order to assess the improvements and the gap which still needs to be fulfilled. It can be done by the end of the training sessions, but it is more favorable to evaluate side by side when the process is still ongoing.
Methods that can be inculcated for evaluation are as follows:
- The Kirkpatrick model
A 4 level model to evaluate L&D
- Reactions
- Learning
- Behavior
- Results
These factors were focused on more when evaluating the performance, how the individuals perceived L&Ds. This model can be implemented to assess the value of individual training programs.
- Brinkerhoff success case method
A focus on systems involving, findings from success cases where individuals’ were benefited from L&Ds which are collected through surveys, performance reports etc. as well as looking at non-success cases which provided no value to employee or the organizations (CIPD, 2021d).
This keen evaluation can aid in better use of methods to be used when filling the gap of leaning needs.
Apart from these evaluations can be done through qualitative approaches where feedback from the line managers and customers can help measure the development and potential gaps for improvement for specific employee or the organization. The feedback can help individuals to devise a plan for improvements and achieve overall productivity.
Appendices
Appendix A: Job Description
| Job Title | People Assistant |
| Department | Human Resource |
| Reporting to | Human Resource Manager |
| Main Purpose of job | To offer decision and technical support in the HR department for the administrative purpose. |
| Key Tasks | To be actively involved in the process of planning the recruiting procedure for new and replacement jobs within the relevant business sector and to assume responsibility for doing so.• To keep detailed records and to monitor every attempt that is made to hire new employees.• To participate in interview panels in order to provide assistance to recruiting managers and to guarantee that the process is conducted objectively.• Responsible for conducting employment checks, which include contacting previous employers for references and determining whether or not the candidate is eligible for the position being applied for• Responsible for gathering all of the information required for payroll purposes and updating the spreadsheet used for payroll prior to the distribution of each month’s salary |
Appendix B: Shortlisting Matrix
Shortlisting Matrix
| Post: People Assistant | Grade:3 | Department/ School:Human Resource Manager |
| Candidate name | E | Intense Knowledge and skills in HR management Principles | Leadership and supervisory skills | Basic Knowlegde on IT proficiency particulaly use of Microsoft Office | Prior Experience of working in a hospital environment | Communication Skills | Interpersonal skills | Scheduling tasks. | Analytical and Decision Making ability. | Total (24) |
| James Floyd | S | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 16 |
| Julius Junk | S | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 2 | Not Shortlisted |
| Philp Stevens | E | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 17 |
| Johnson Brown | N | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 19 |
Shortlisting panel members:
Name: James Richard Job Title: HR Manager Signature: Date: 10 Oct 2022
Name: Josephine Leon Job Title: Supervisor Signature: Date: 10 Oct 2022
References
Amanda Sellers, 2021. The AIDA Model: A Proven Framework for Converting Strangers into Customers. Available at https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/aida-model#:~:text=The%20stages%20are%20Attention%2C%20Interest,to%20try%20or%20buy%20it.
Arifin, Z., Nirwanto, N. and Manan, A., 2019. Improving the effect of work satisfaction on job performance through employee engagement. International Journal of Multi-Discipline Science (IJ-MDS), 2(1), pp.1-9.
Barker PhD, K., Diversity and Inclusion in International Communications: Applications for Today’s Work World. Global Advances in Business Communication, 9(1), p.4.
Caporarello, L., Manzoni, B. and Panariello, B., 2019, June. Learning and development is the key. How well are companies doing to facilitate employees’ learning?. In International Conference in Methodologies and intelligent Systems for Techhnology Enhanced Learning (pp. 80-88). Springer, Cham.
Cattermole, G., 2019. Developing the employee lifecycle to keep top talent. Strategic HR review.
CIPD, 2021b. Selection methods. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/recruitment/selection-factsheet#gref
CIPD, 2021c. Coaching and mentoring. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/development/coaching-mentoring-factsheet
CIPD, 2021d. Evaluating learning and development. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/development/evaluating-learning-factsheet#gref
CIPD, 2021a. Recruitment: an introduction. Available at https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/people/recruitment/factsheet#gref
Cléry-Melin, M.L., Jollant, F. and Gorwood, P., 2019. Reward systems and cognitions in Major Depressive Disorder. CNS spectrums, 24(1), pp.64-77.
Diamantidis, A.D. and Chatzoglou, P., 2018. Factors affecting employee performance: an empirical approach. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management.
Fazilah, S., Mohamad, A.A.A. and Hamid, Z.A., 2019. Monetary compensation as a remedy for unfair dismissal: a study in United Kingdom and Malaysia. IIUM Law Journal, 27(2), pp.447-468.
Gupta, S., 2019. Challenges Faced by Adecco Employees in Handling Employee Lifecycle. In Proceedings of 10th International Conference on Digital Strategies for Organizational Success.
Haddon, J., 2018. The impact of employees’ well-being on performance in the workplace. Strategic HR Review.
Jackson, D. and Collings, D., 2018. The influence of work-integrated learning and paid work during studies on graduate employment and underemployment. Higher Education, 76(3), pp.403-425.
Kamalaveni, M., Ramesh, S. and Vetrivel, T., 2019. A review of literature on employee retention. International Journal of Innovative Research in Management Studies (IJIRMS), 4(4), pp.1-10.
Mani, V., 2012. The effectiveness of employee referral as a recruitment source. International Journal of Management Sciences and Business Research, 1(11).
Mokhinur, B., 2020. A thorough review of the common law concept of” arbitrary termination” and” unfair dismissal”(including difc&adgm. Review of law sciences, (November Еxclusive issue), pp.77-89.
Newell, S., 2005. Recruitment and selection. Managing human resources: Personnel management in transition, pp.115-147.
Nguyen, T.M. and Prentice, C., 2022. Reverse relationship between reward, knowledge sharing and performance. Knowledge Management Research & Practice, 20(4), pp.516-527.
Nyarko, C.B., 2020. Effect of Reward on Employee Retention at Takoradi Technical University (Doctoral dissertation, University of Cape Coast).
Odor, H. O. (2018). A literature review on organizational learning and learning organizations. International Journal of Economics & Management Sciences, 7(1), 1-6.
Orridge, S. and Madderson, N., 2021. Equality and diversity policy. Policy, 1(02).
Paine, N. (2021). Workplace learning: How to build a culture of continuous employee development. Kogan Page Publishers.
Poulose, S. and Dhal, M., 2020. Role of perceived work–life balance between work overload and career commitment. Journal of Managerial Psychology.
Pulakos, E.D., Mueller-Hanson, R. and Arad, S., 2019. The evolution of performance management: Searching for value. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 6, pp.249-271.
Sarah Cook, n.d. Linking Learning Needs Analysis to Business Needs. Available at https://www.thestairway.co.uk/publications/linking-learning-needs-analysis-to-business-needs.html
Shanock, L. R., Eisenberger, R., Heggestad, E. D., Malone, G., Clark, L., Dunn, A. M., … & Woznyj, H. (2019). Treating employees well: The value of organizational support theory in human resource management. The Psychologist-Manager Journal, 22(3-4), 168.
Simonsen, K.A. and Shim, R.S., 2019. Embracing diversity and inclusion in psychiatry leadership. Psychiatric Clinics, 42(3), pp.463-471.
Srichailard, P., Wannasawade, W. and Sintanakul, K., 2019. A conceptual framework of project-based learning by analyzing of VARK. Interdisciplinary Research Review, 14(5), pp.1-6.
Tziner, A. and Rabenu, E., 2018. Beyond performance appraisal: To performance management and firm-level performance. In Improving Performance Appraisal at Work. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Younas, W., Farooq, M., Khalil-Ur-Rehman, F. and Zreen, A., 2018. The impact of training and development on employee performance. IOSR Journal of Business and Management (IOSR-JBM), 20(7), pp.20-23.
Contents
- 1 AC 2.1 Different selection methods and when it is appropriate to use them
- 2 AC 2.4 Explain the selection records that need to be retained
- 3 AC 2.5 Write letters of appointment and non-appointment for an identified role
- 4 Task 2 Simulated interview
- 5 AC 2.2 Devise selection criteria for the post of People Assistant using the job description (Appendix A). Use the selection shortlisting matrix (Appendix B) to shortlist applications against the selection criteria to determine candidates to be interviewed.
- 6 AC 2.3 Interview of one applicant and decide whether they meet the criteria for the post. The interview could be a panel or one-to-one interview. The interview could be conducted face-to-face, by telephone or by web conferencing.
- 7 TASK 3 Guidance Document
- 8 AC 3.1 An explanation of the importance of achieving work-life balance within the employment relationship with an overview of the regulations relevant to work-life balance.
- 9 AC 3.2 An explanation of what is meant by, and the importance of, wellbeing in the workplace.
- 10 AC 3.3 A summary of the main points of discrimination legislation
- 11 AC 3.4 An explanation of what diversity and inclusion mean and why they are important
- 12 AC 3.5 An explanation of the difference between fair and unfair dismissal
- 13 TASK 4 briefing paper
- 14 AC 4.2 Explain the main factors that need to be considered when managing performance
- 15 AC 4.3 Explain different methods of performance review
- 16 AC 5.1 Explanation of key components (financial and non-financial) that are required to achieve an effective total reward system
- 17 AC 5.2 Explanation of the relationship between reward and performance and the links to motivation
- 18 AC 5.3 Reasons to Treat Employees Fairly In Retention to Pay
- 19 TASK 5
- 20 Overview
- 21 AC 6.1 Explanation why learning and development activities are of benefit to individuals and organizations
- 22 AC 6.2 Description of different types of learning needs and reasons why they arise for individuals and organisations
- 23 AC 6.3 Summary of different face-to-face and blended learning and development approaches
- 24 AC 6.4 Explanation of how individual requirements and preferences must be accommodated in the design and delivery of learning and development
- 25 AC 6.5 Discussion of how learning and development can be evaluated
- 26 Appendices
- 27 Appendix A: Job Description
- 28 Appendix B: Shortlisting Matrix
Download the Full 3CO04 Example
Get instant access to the complete assignment by unlocking below.
References
Chión, S.J., Charles, V. & Morales, J., 2020. The impact of organisational culture, organisational structure, and technological infrastructure on process improvement through knowledge sharing. Business Process Management Journal, 26(6), pp.1443–1472.
Islam, T., Islam, R., Pitafi, A.H., Xiaobei, L., Rehmani, M., Irfan, M. & Mubarak, M.S., 2021. The impact of corporate social responsibility on customer loyalty. Sustainable Production and Consumption, 25, pp.123–135.
Laig, R.B.D. & Abocejo, F.T., 2021. Change management process in a mining company. Journal of Business and Management Studies, 3(1), pp.118–133.
Nudurupati, S.S., Garengo, P. & Bititci, U.S., 2021. Impact of the changing business environment on performance measurement and management practices. International Journal of Production Economics, 232, p.107942.
+ 16 more references included in the full download.